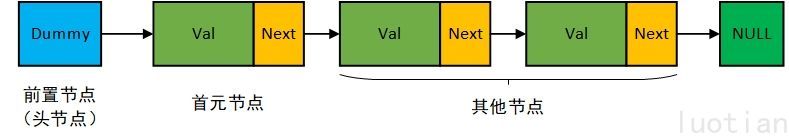
对于一个链表,C++ 的定义如下:
struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode () : val (0 ), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x) : val (x), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x, ListNode *next) : val (x), next (next) {} };
链表结构可由下表征:
力扣 203
移除链表元素
ListNode* removeElements (ListNode* head, int val) struct ListNode * dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); struct ListNode * temp = dummy; while (temp->next != NULL ) { if (temp->next->val == val) { temp->next = temp->next->next; } else { temp = temp->next; } } return dummy->next; }
时间复杂度为 $\small {O (n)}$,空间复杂度为 $\small {O (1)}$。
力扣 707
设计链表
class MyLinkedList {public : MyLinkedList () { this ->head = new ListNode (0 ); this ->size = 0 ; } int get (int index) if (index < 0 || index >= size) { return -1 ; } ListNode* cur = head; for (int i = 0 ; i <= index; i++) { cur = cur->next; } return cur->val; } void addAtHead (int val) addAtIndex (0 , val); } void addAtTail (int val) addAtIndex (size, val); } void addAtIndex (int index, int val) if (index > size) return ; index = max (0 , index); size++; ListNode* temp = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { temp = temp->next; } ListNode* NewNode = new ListNode (val); NewNode->next = temp->next; temp->next = NewNode; } void deleteAtIndex (int index) if (index < 0 || index >= size) return ; size--; ListNode* temp = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { temp = temp->next; } ListNode* p = temp->next; temp->next = temp->next->next; delete p; } private : struct ListNode { int val; ListNode* next; ListNode () : val (0 ), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x) : val (x), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x, ListNode* next) : val (x), next (next) {} }; int size; ListNode* head; };
力扣 206
反转链表
ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) ListNode* slow = NULL ; ListNode* fast = head; while (fast != NULL ) { ListNode* temp = fast->next; fast->next = slow; slow = fast; fast = temp; } return slow; }
力扣 24
两两交换链表中的节点
ListNode* swapPairs (ListNode* head) ListNode* dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode* temp = dummy; while (temp->next != NULL && temp->next->next != NULL ) { ListNode* node1 = temp->next; ListNode* node2 = temp->next->next; temp->next = node2; node1->next = node2->next; node2->next = node1; temp = node1; } ListNode* res = dummy->next; delete dummy; return res; }
力扣 19
删除链表倒数第 N 个节点
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd (ListNode* head, int n) ListNode* fast = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode* slow = fast; ListNode* dummy = fast; if (n <= 0 ) { return dummy->next; } for (int count = 1 ; count <= n; count++) { if (fast->next != NULL ) { fast = fast->next; } else if (count < n) { return slow->next; } } while (fast->next != NULL ) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } ListNode* temp = slow->next; slow->next = slow->next->next; delete temp; return dummy->next; }
时间复杂度为 $\small {O (L)}$,$\small {L}$ 为链表长度。空间复杂度为 $\small {O (1)}$。
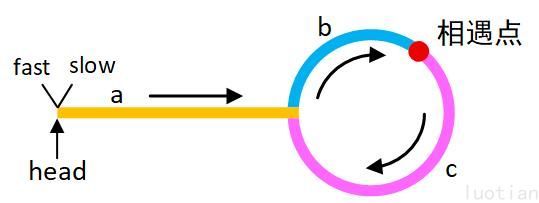
力扣 142
环形链表 Ⅱ
ListNode *detectCycle (ListNode *head) ListNode* fast = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode* slow = fast; while (fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL ) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if (fast->next == slow->next) { ListNode* index = head; slow = slow->next; while (index != slow) { index = index->next; slow = slow->next; } return index; } } return nullptr ; }
力扣 15
三数之和
int i = 0 ; i < nums.size ();int left = i + 1 ;int right = nums.size () - 1 ;
这里没有说返回的数组是有序的,那么可以先对数组从小到大进行排序,然后再遍历数组,这样做是因为三数相加为 0,也就是 $\small {a + b+c = 0}$,$\small {a\leqslant b\leqslant c}$。那么一定有 $\small {a\leqslant 0}$,因此有了第一个判断条件,如果 nums [i] > 0,直接返回结果,不用再遍历了。
vector<vector<int >> threeSum (vector<int >& nums) { vector<vector<int >> res; sort (nums.begin (), nums.end ()); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { if (nums[i] > 0 ) return res; if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) continue ; int left = i + 1 ; int right = nums.size () - 1 ; while (right > left) { if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0 ) right--; else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0 ) left++; else { res.push_back (vector<int >{nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]}); while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--; while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++; right--; left++; } } } return res; }
时间复杂度是 $\small {O (N^2)}$。
力扣 18
四数之和
vector<vector<int >> fourSum (vector<int >& nums, int target) { vector<vector<int >> res; sort (nums.begin (), nums.end ()); for (int k = 0 ; k < nums.size (); k++) { if (nums[k] > target && (nums[k] >= 0 || target >= 0 )) break ; if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1 ]) continue ; for (int i = k + 1 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { if (nums[k] + nums[i] > target && nums[i] >= 0 ) break ; if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && i > k + 1 ) continue ; int left = i + 1 ; int right = nums.size () - 1 ; while (right > left) { if ((long )nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target) right--; else if ((long )nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target) left++; else { res.push_back (vector<int >{nums[k], nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]}); while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--; while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++; right--; left++; } } } } return res; }